About us
A synergy between clinical experience and ongoing commitment to scientific research.


Our scientific publications
Doliveux R, Doliveux S.
2024 April - Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants.
Guided and Prosthetically Driven Bone Augmentation Using the Shell Technique and Allogeneic Cortical Plate: A Prospective Case Series
Abstract
Purpose: To describe the use of digital technology to surgically guide the shell technique using allogenic cortical plates for a fully guided bone augmentation procedure.
Materials and methods: A total of 10 patients who required bone augmentation for implant placement were included in this study. Allogenic cortical plates were planned using CAD/CAM to have identical thickness to the original cortical plates, then were digitally positioned and shaped to outline the bone defect according to the existing anatomical details. A cutting pattern and a surgical template were manufactured according to the digitally preplanned bone graft and the intraoral setting.
Results: A total of 12 horizontal bone grafting procedures were performed using the shell technique with allogenic cortical plates. All grafting procedures were deemed successful and allowed for ideal 3D implant positioning. Of the 12 bone grafting procedures, which used a surgical template to position the cortical plate, 3 required an adjustment to reposition the plate to a more ideal position.
Conclusion: Digital technology was used to create a surgical template to guide the shell bone grafting technique with allogenic cortical plates. All surgical templates offered a fixed support to hold the cortical allogenic plate in the preplanned position, offering a predictable, simplified, and accurate guided bone grafting procedure. Further studies on a larger population of patients are necessary to assess those results and to verify the treatment approach described in this study.
Keywords: bone grafting; computer-guided surgery; shell technique.
El Kholy K, Doliveux S, Mattheos N, Buser D.
2023 September - Int J Prosthodont.
Preplanned Computer-Assisted Advanced Implant Placement for Orthodontic Patients: Presentation of a Novel Multidisciplinary Treatment Approach and a Case Report
Abstract
This case report describes a novel approach combining orthodontic and implant digital treatment planning workflows to enable prosthetically driven implant placement before orthodontic treatment is performed or completed. The computer-assisted implant placement is performed using a static surgical guide based on the future positions of the teeth after completion of orthodontic treatment. This innovative approach allows for select partially edentulous patients to undergo fixed prosthetic rehabilitation before orthodontic treatment is completed.
Doliveux S, Jamjoom FZ, Albahri R, Rousson DD, Hamilton A, El Kholy K.
2023 January - Int J Prosthodont.
Complete-Arch Implant Rehabilitation with the Aid of Computer-Assisted Implant Surgery and Transitional Implants: A New Digital Approach
Abstract
This case report describes a new digital workflow for computer-assisted implant surgery in an edentulous patient using transitional implants to support a fixed surgical template and interim prosthesis. The accuracy of the final implant position using the described protocol was evaluated and compared to the outcomes obtained using other types of surgical templates. This novel digital approach appears to enhance the accuracy of implant positioning for edentulous patients and seems to be comparable to a tooth-supported surgical template.
Hamilton A, Obermaier B, Doliveux S, Negreiros WM, Alnasser M, Gallucci GO.
2022 January - Int J Prosthodont.
Digitally Fabricated Provisional Implant Restorations Prior to Implant Placement: A Clinical Case Series
Abstract
Purpose: To review the factors that affect the ability to deliver a CAD/CAM implant-supported provisional restoration designed from a virtually planned implant position prior to surgical placement with static computer-assisted implant surgery (sCAIS).
Materials and methods: Data were collected on patients treated with single-tooth implant treatment in which CBCT was combined with intraoral scans and imported into a virtual implant planning software. A synchronization tool established the connection between the planning software and the CAD software, where a digital diagnostic tooth arrangement was performed to create the ideal tooth dimensions and mucosal architecture. The virtual implant planning was finalized, and the implant position was transferred to the CAD software, where a restoration was designed and fabricated. The sCAIS was performed, and the prefabricated custom restorations were delivered on the day of the surgery or following healing if delayed loading or submerged healing was required. Descriptive statistics and statistical comparison with two-proportion z test were performed.
Results: A total of 23 patients with 28 single-implant sites met the inclusion criteria and were included in the study. Nineteen customized healing abutments and 10 provisional crowns were designed and fabricated for a total of 29 restorations. Of the restorations, 23 were successfully delivered on the day of the surgical intervention. No statistical significance was found among the different variables compared.
Conclusion: Custom prefabricated CAD/CAM restorations based on a virtually planned implant position can be successfully designed, fabricated, and delivered when used in combination with sCAIS.
Doliveux S, Jamjoom FZ, Finelle G, Hamilton A, Gallucci GO.
2020 January - Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants.
Preservation of Soft Tissue Contours Using Computer-Aided Design/Computer-Assisted Manufacturing Healing Abutment with Guided Surgery in the Esthetic Area: Case Report
Abstract
This case report describes a digital workflow for a computer-aided design/computer-assisted manufacturing (CAD/CAM) healing abutment used in immediate implant placement in the esthetic zone. The design of the healing abutment was based on the existing tooth anatomy in order to provide anatomical support to the gingival tissues and to preserve the gingival contours of the natural tooth. This approach enhances the esthetic outcome of the definitive implant restoration. The surgical procedure including the guided bone regeneration is simplified, postoperative morbidity is reduced, and excessive occlusal loading during healing is limited.
Jamjoom FZ, Doliveux S, Rousson DD, Friedland B, Hamilton A.
2019 September - Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants.
A Modified Implant Surgical Guide for the Administration of Maxillary Nerve Block Anesthesia Intraorally via the Greater Palatine Foramen: Case Report
Abstract
Block anesthesia for the maxillary division (V2) of the trigeminal nerve is a suitable approach when an entire quadrant of teeth and/or associated structures are involved. The most effective approach to anesthetize the maxillary branch is intraorally via the greater palatine canal. This case report describes the use of a computer-aided design/computer-assisted manufacturing (CAD/CAM) implant surgical template designed with a guide channel to allow for the administration of maxillary nerve block through the greater palatine canal.
Doliveux S, Jamjoom FZ, Nadra M, Gallucci GO, Hamilton A.
2020 April - J Prosthet Dent.
Fabrication technique for a custom implant emergence profile on 3D printed casts
Abstract
A procedure is described for fabricating a removable resilient soft-tissue replica that accurately replicates the contoured emergence profile of an interim implant-supported restoration on a cast fabricated by 3D printing. The technique uses digital scanning and 3D printing technologies to produce a 3D printed replica of the implant-supported interim crown, which is then used to fabricate the custom soft-tissue replica. This straightforward technique allows the accurate replication of the emergence profile without retaining the interim crown or fabricating a new one. No additional clinical appointments are needed.
Hamilton A, Jamjoom F, Doliveux S, Gallucci GO, Friedland B.
2019 July - J Prosthet Dent.
Radiographic markers for merging virtual data sets
Abstract
A procedure for registering digital intraoral surface scans onto cone beam computed tomography in the presence of significant scatter artifact is described. The technique uses chairside-fabricated composite resin markers placed on well-distributed teeth to serve as common landmarks in each digital data set for accurate registration. This straightforward, noninvasive, and cost-effective technique facilitates registration without the need for a specialized armamentarium or radiographic templates.
El Kholy K, Doliveux S, Mattheos N, Buser D.
2023 September - Int J Prosthodont.
Preplanned Computer-Assisted Advanced Implant Placement for Orthodontic Patients: Presentation of a Novel Multidisciplinary Treatment Approach and a Case Report
Abstract
This case report describes a novel approach combining orthodontic and implant digital treatment planning workflows to enable prosthetically driven implant placement before orthodontic treatment is performed or completed. The computer-assisted implant placement is performed using a static surgical guide based on the future positions of the teeth after completion of orthodontic treatment. This innovative approach allows for select partially edentulous patients to undergo fixed prosthetic rehabilitation before orthodontic treatment is completed.
Doliveux S, Jamjoom FZ, Albahri R, Rousson DD, Hamilton A, El Kholy K.
2023 January - Int J Prosthodont.
Complete-Arch Implant Rehabilitation with the Aid of Computer-Assisted Implant Surgery and Transitional Implants: A New Digital Approach
Abstract
This case report describes a new digital workflow for computer-assisted implant surgery in an edentulous patient using transitional implants to support a fixed surgical template and interim prosthesis. The accuracy of the final implant position using the described protocol was evaluated and compared to the outcomes obtained using other types of surgical templates. This novel digital approach appears to enhance the accuracy of implant positioning for edentulous patients and seems to be comparable to a tooth-supported surgical template.
De Poi RP, Kowolik M, Oshida Y, El Kholy K.
2021 June - Front Immunol.
The Oxidative Response of Human Monocytes to Surface Modified Commercially Pure Titanium
Abstract
Cellular responses to implanted biomaterials are key to understanding osseointegration. The aim of this investigation was to determine the in vitro priming and activation of the respiratory burst activity of monocytes in response to surface-modified titanium. Human peripheral blood monocytes of healthy blood donors were separated, then incubated with surface-modified grade 2 commercially pure titanium (CPT) disks with a range of known surface energies and surface roughness for 30- or 60-min.
Secondary stimulation by phorbol 12-myrisate 13-acetate (PMA) following the priming phase, and luminol-enhanced-chemiluminescence (LCL) was used to monitor oxygen-dependent activity. Comparison among groups was made by incubation time using one-way ANOVA. One sample from each group for each phase of the experiment was viewed under scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and qualitative comparisons made.
The results indicate that titanium is capable of priming peripheral blood monocytes following 60-min incubation. In contrast, 30 min incubation time lead to reduced LCL on secondary stimulation as compared to cells alone. At both time intervals, the disk with the lowest surface energy produced significantly less LCL compared to other samples. SEM examination revealed differences in surface morphology at different time points but not between differently surface-modified disks. These results are consistent with the hypothesis that the titanium surface characteristics influenced the monocyte activity, which may be important in regulating the healing response to these materials.
Keywords: Chemiluminescence; dental implants; monocytes; oxidative response; surface energy; surface roughness; titanium; wettability.
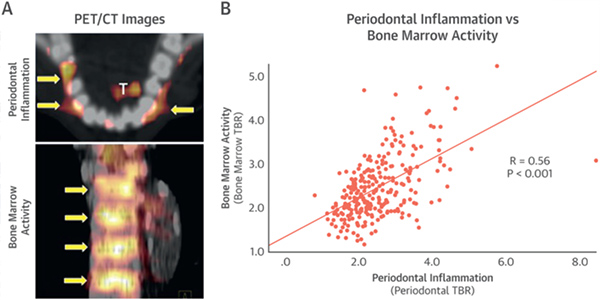
Van Dyke TE, Kholy KE, Ishai A, Takx RAP, Mezue K, Abohashem SM, Ali A, Yuan N, Hsue P, Osborne MT, Tawakol A.
2021 March - J Periodontol.
Inflammation of the periodontium associates with risk of future cardiovascular events
Abstract
Background: While growing evidence suggests a link between periodontal disease (PD) and cardiovascular disease (CVD), the independence of this association and the pathway remain unclear. Herein, we tested the hypotheses that: (1) inflammation of the periodontium (PDinflammation ) predicts future CVD independently of disease risk factors shared between CVD and PD, and (2) the mechanism linking the two diseases involves heightened arterial inflammation.
Methods: Data were collected on patients treated with single-tooth implant treatment in which CBCT was combined with intraoral scans and imported into a virtual implant planning software. A synchronization tool established the connection between the planning software and the CAD software, where a digital diagnostic tooth arrangement was performed to create the ideal tooth dimensions and mucosal architecture. The virtual implant planning was finalized, and the implant position was transferred to the CAD software, where a restoration was designed and fabricated. The sCAIS was performed, and the prefabricated custom restorations were delivered on the day of the surgery or following healing if delayed loading or submerged healing was required. Descriptive statistics and statistical comparison with two-proportion z test were performed.
Results: A total of 23 patients with 28 single-implant sites met the inclusion criteria and were included in the study. Nineteen customized healing abutments and 10 provisional crowns were designed and fabricated for a total of 29 restorations. Of the restorations, 23 were successfully delivered on the day of the surgical intervention. No statistical significance was found among the different variables compared.
Conclusion: PDinflammation is independently associated with MACE via a mechanism that may involve increased arterial inflammation. These findings provide important support for an independent relationship between PDinflammation and CVD.
Keywords: atherosclerosis; cardiovascular disease; positron emission tomography; periodontal disease.
El Kholy K, Buser D, Wittneben JG, Bosshardt DD, Van Dyke TE, Kowolik MJ.
2020 August - Materials (Basel).
Investigating the Response of Human Neutrophils to Hydrophilic and Hydrophobic Micro-Rough Titanium Surfaces
Abstract
Various treatments have been used to change both the topography and chemistry of titanium surfaces, aiming to enhance tissue response and reduce healing times of endosseous implants. Most studies to date focused on bone healing around dental implants occurring later during the healing cascade.
However, the impact of the initial inflammatory response in the surgical wound site on the success and healing time of dental implants is crucial for implant integration and success, yet it is still poorly understood. The purpose of this study was to investigate the effect of titanium surface hydrophilicity on the response of human neutrophils by monitoring oxygen radical production, which was measured as chemiluminescence activity.
Materials and Methods: Neutrophils were isolated from human donors' blood buffy coats using the double sucrose gradient method. Neutrophils were exposed to both hydrophilic and hydrophobic titanium surfaces with identical topographies in the presence and absence of human serum. This resulted in six experimental groups including two different implant surfaces, with and without exposure to human serum, and two control groups including an active control with cells alone and a passive control with no cells. Two samples from each group were fixed and analyzed by SEM. Comparisons between surface treatments for differences in chemiluminescence values were performed using analysis of variance ANOVA. Results and Conclusion: In the absence of exposure to serum, there was no significant difference noted between the reaction of neutrophils to hydrophilic and hydrophobic surfaces. However, there was a significant reduction in the mean and active chemiluminescence activity of neutrophils to serum-coated hydrophilic titanium surfaces than to serum-coated hydrophobic titanium surfaces. This suggests that surface hydrophilicity promotes enhanced adsorption of serum proteins, which leads to decreased provocation of initial immune cells and reduction of local oxygen radical production during wound healing. This can help explain the faster osseointegration demonstrated by hydrophilic titanium implants.
Ducommun J, El Kholy K, Rahman L, Schimmel M, Chappuis V, Buser D.
2019 November - Clin Oral Implants Res.
Analysis of trends in implant therapy at a surgical specialty clinic: Patient pool, indications, surgical procedures, and rate of early failures-A 15-year retrospective analysis
Abstract
Objective: To evaluate the patient population over a 3-year period and to compare it to observations of the population at the same clinic over a period of 15 years.
Materials and methods: Records of patients receiving dental implants in the Department of Oral Surgery and Stomatology, University of Bern, between January 2014 and December 2016 were analyzed and then compared with data from patients treated between 2002 and 2004 and between 2008 and 2010. Patients were analyzed for demographics and for indications for therapy, as well as for presence or absence and type of complications. Inserted implants were analyzed for type, length, and diameter, as well as for the number and type of associated tissue regeneration procedures.
Results: Analysis revealed a continuous linear increase in the average age of patients seeking implant treatment. The most common indication for implant therapy was a single-tooth gap (STG) (50.5%), followed by distal extension situations (22.3%) and extended edentulous gaps (20.5%). A total of 60.8% of implants placed needed some type of bone augmentation, and 83.5% of implants placed in the anterior maxilla required simultaneous augmentation. Staged guided bone regeneration (GBR) was only necessary in 7% of the cases. Implant failure rates remained low at 0.6%, with postoperative hematomas being the most common postoperative complication (13.4%).
Conclusion: The rising demand for dental implants continues as the patient population ages. Single-tooth gaps remained consistently the most common indication for implant therapy in recent years. Proper case selection and evidence-based surgical protocols are essential for high success rates.
El Kholy K, Lazarin R, Janner SFM, Faerber K, Buser R, Buser D.
2019 November - Clin Oral Implants Res.
Influence of surgical guide support and implant site location on accuracy of static Computer-Assisted Implant Surgery
Abstract
Objective: To investigate the effect of surgical guide support and implant site location on the accuracy of static Computer-Assisted Implant Surgery (sCAIS) in partially edentulous patients.
Materials and methods: 375 replica implants were inserted in 85 study models. Surgical implant placement was done using static 3D printed surgical guides, which were designed to be supported either by all the teeth present in the model (full arch), or by 4-teeth), 3-teeth or 2-teeth. Each study model included three single-tooth gap (STG) situations; one extraction socket site and two implants placed in a distal extension situation. Preplanned and postoperative implant positions were compared using the treatment-evaluation tool in digital software. 3-dimensional and angular deviations were measured. Statistical analysis was done using ANOVA, and pairwise t tests and Bonferroni-Holm's adjustment were applied as a post hoc test.
Results: Accuracy of surgical guides used in sCAIS was significantly affected by the number and type of teeth used for its support. Guides supported by 4 teeth were not significantly different from accuracy of full-arch-supported guides (p > .05). Guide support by posterior teeth was associated with an increased level of accuracy, when compared to anterior teeth guide support. Implants placed in extraction sockets were associated with significantly higher 3D and angular deviation values, and surgical guides with a distal extension situation resulted in significantly higher deviation values
Conclusion: The number and location of teeth supporting the surgical guide can significantly influence the accuracy of sCAIS, with 4 teeth providing equal accuracy to full-arch guides in (STG) situations.
Keywords: Computer-Assisted; guide support; guided surgery; implantology; surgical guide.
El Kholy K, Ebenezer S, Wittneben JG, Lazarin R, Rousson D, Buser D.
2019 October - Clin Implant Dent Relat Res.
Influence of implant macrodesign and insertion connection technology on the accuracy of static computer-assisted implant surgery
Abstract
Objective: The aim of this study was to evaluate the effect of three different macrodesigns and two different insertion devices on the accuracy of static computer-assisted implant surgery (sCAIS).
Materials and methods: Ninety implant replicas with three different macrodesigns: Soft tissue level (TL), bone level (BL), and bone level tapered (BLT) were placed in 30 dental models with two implant insertion devices: Guided adapter and guided screwed-in mount. Preoperative and postoperative positions of implants were compared and the mean angular deviation, crestal, and apical three-dimensional (3D) deviation were calculated for each implant macrodesign and each insertion device. Data were analyzed using analysis of variance, post hoc t-tests and Bonferroni-Holm's adjustment method. P values less than .05 were considered statistically significant.
Results: BLT implants had lower mean 3D deviation values at the crest and the apex when compared with 3D deviations with BL and TL implants Also, BLT implants had lower angular deviations, when compared with BL and TL Implants, however, angular deviations were not statistically significant Considering the insertion device method, no significant differences were noted between insertion devices irrespective of the deviation analyzed.
Conclusion: The macrodesign of dental implants may have an influence on the accuracy of sCAIS, with tapered designs offering slightly better positional accuracy than parallel-walled macrodesigns independent on the method of insertion used.
Keywords: accuracy; computer-aided; computer-assisted; digital; guided surgery; implant; implant design; implant surgery; implantology.
El Kholy K, Janner SFM, Schimmel M, Buser D.
2019 February - Clin Implant Dent Relat Res.
The influence of guided sleeve height, drilling distance, and drilling key length on the accuracy of static Computer-Assisted Implant Surgery.
Abstract
Objective: The aim of this systematic review and meta-analysis was to compare the clinical efficacy of the early dental implant placement protocol with immediate and delayed dental implant placement protocols.
Materials and methods: Pre and post-operative positions of implants placed in duplicate dental models were compared and recorded after placement of implants according to a standardized treatment planning and execution sCAIS protocol. Guided sleeve heights: 2 mm, 4 mm, 6 mm and guided key heights: 1 mm and 3 mm were equally randomized in six test groups with varying implant lengths (10-16 mm) and surgical drilling protocols. The mean crestal and apical three-dimensional (3D) deviation, as well as the angular deviation were calculated for each group. Data was analyzed using multivariate analysis anova. P values less than .05 were considered statistically significant. All P values of post-hoc tests were corrected for multiple testing using Bonferroni-Holm's adjustment method.
Results: 3D implant positioning accuracy was not significantly affected by the difference in sleeve height alone or by the implant length alone (P > .05). However, 3D and angular deviation values became significantly higher as the total drilling distance below the guided sleeve increased and significantly became lower as the guided key height above the sleeve increased. 18 mm drilling distance resulted in a significantly higher deviation, when compared to 14 mm or 16 mm drilling distances, irrespective of sleeve height or implant length. 3 mm key height resulted in significantly less 3D deviation than 1 mm key height.
Conclusion: Decreasing the drilling distance below the guided sleeve, by using shorter sleeve heights or shorter implants can significantly increase the accuracy of sCAIS.
Keywords: accuracy; computer assisted; computer-aided; dental implants; digital workflow; free drilling distance; guided surgery; implant; implant surgery; implantology; surgical techniques.
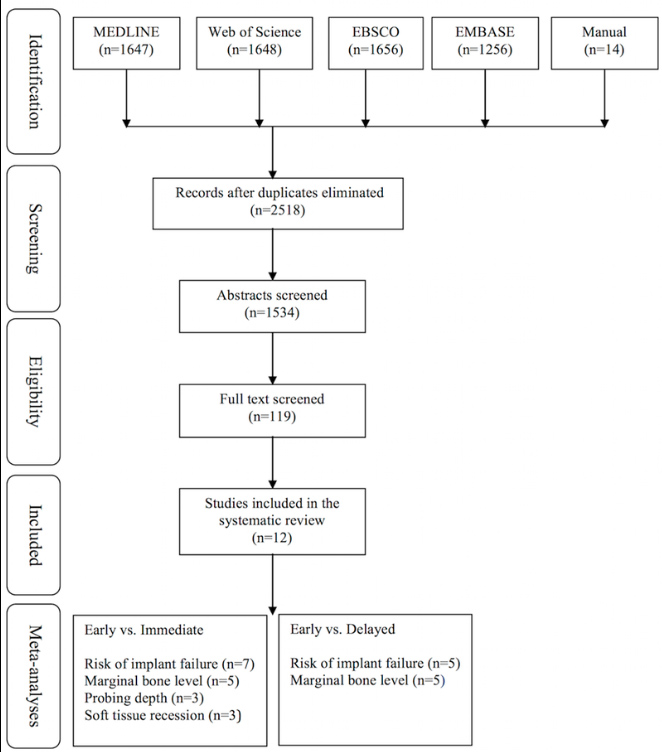
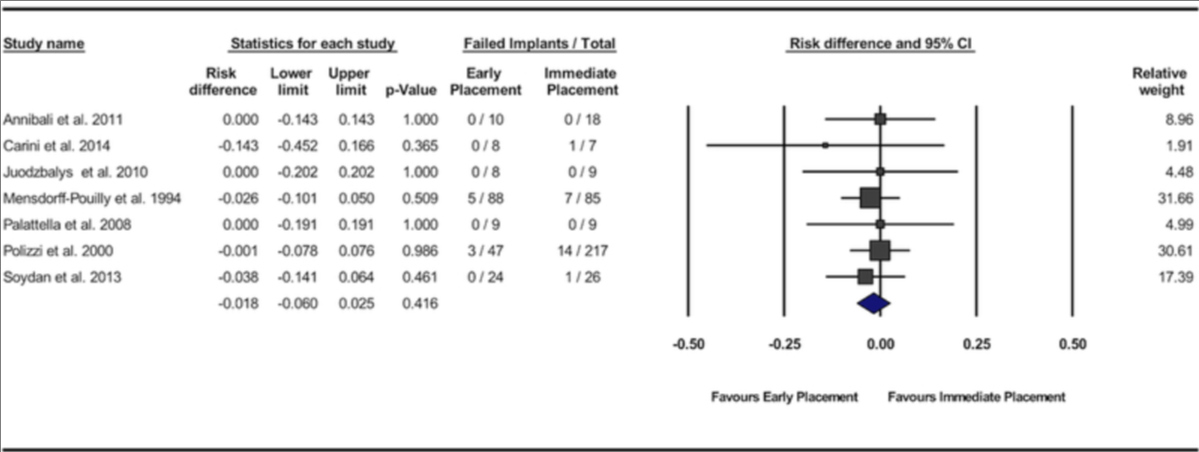
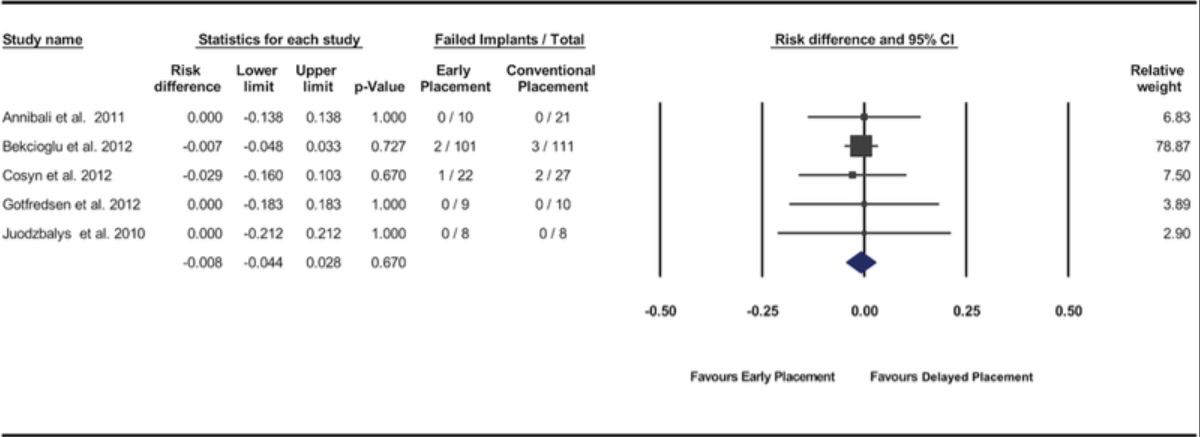
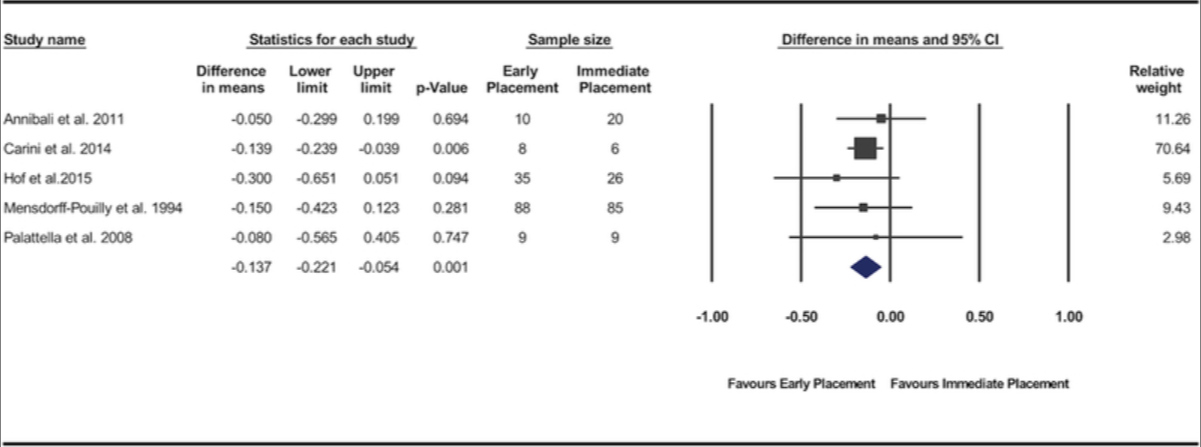
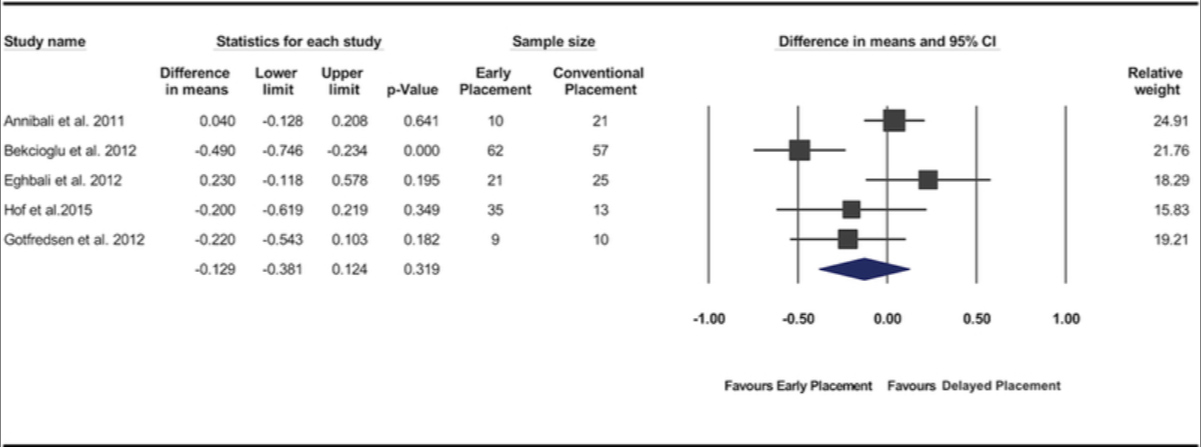
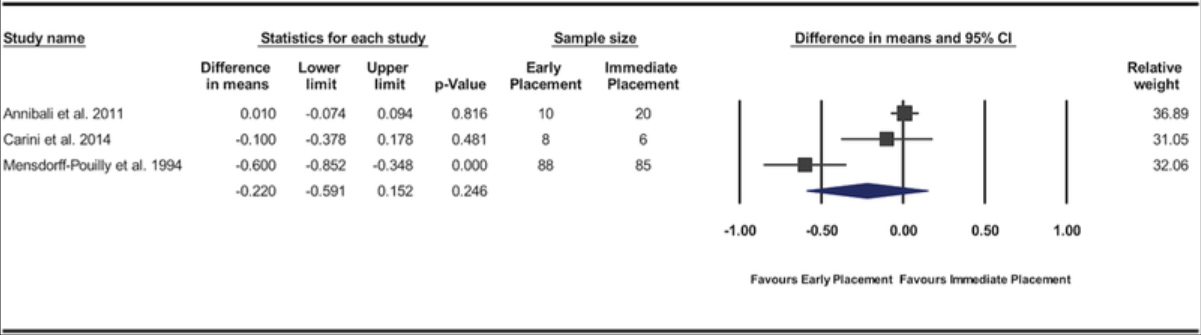
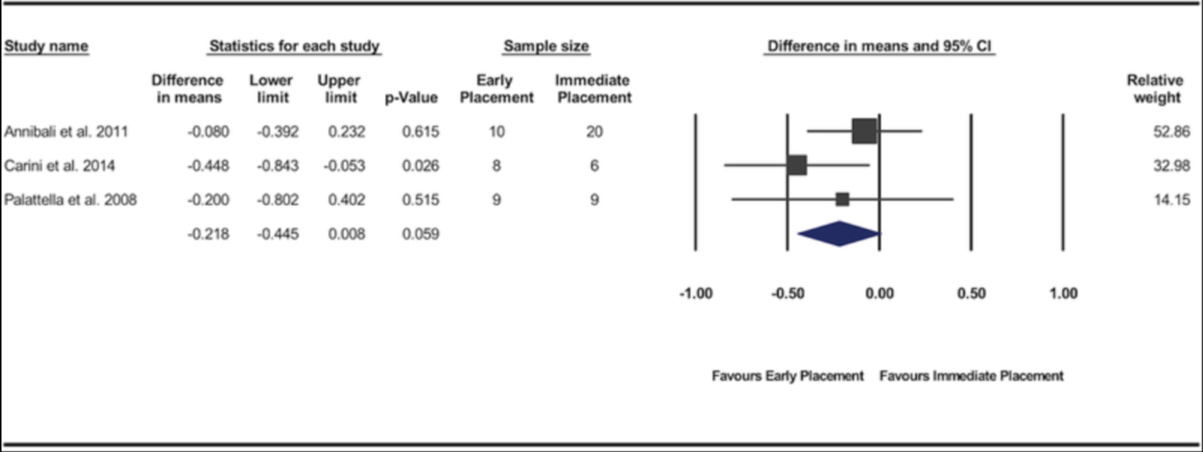
Bassir SH, El Kholy K, Chen CY, Lee KH, Intini G.
2019 May - J Periodontol.
Outcome of early dental implant placement versus other dental implant placement protocols: A systematic review and meta-analysis.
Abstract
Background: The aim of this systematic review and meta-analysis was to compare the clinical efficacy of the early dental implant placement protocol with immediate and delayed dental implant placement protocols.
Methods: An electronic and manual search of literature was made to identify clinical studies comparing early implant placement with immediate or delayed placement. Data from the included studies were pooled and quantitative analyses were performed for the implant outcomes reported as the number of failed implants (primary outcome variable) and for changes in peri-implant marginal bone level, peri-implant probing depth, and peri-implant soft tissue level (secondary outcome variables).
Results: Twelve studies met the inclusion criteria. Significant difference in risk of implant failure was found neither between the early and immediate placement protocols (risk difference = -0.018; 95% confidence interval [CI] = -0.06, 0.025; P = 0.416) nor between early and delayed placement protocols (risk difference = -0.008; 95% CI = -0.044, 0.028; P = 0.670). Pooled data of changes in peri-implant marginal bone level demonstrated significantly less marginal bone loss for implants placed using the early placement protocol compared with those placed in fresh extraction sockets (P = 0.001; weighted mean difference = -0.14 mm; 95% CI = -0.22, -0.05). No significant differences were found between the protocols for the other variables.
Conclusions: The available evidence supports the clinical efficacy of the early implant placement protocol. Present findings indicate that the early implant placement protocol results in implant outcomes similar to immediate and delayed placement protocols and a superior stability of peri-implant hard tissue compared with immediate implant placement.
Keywords: clinical protocols; dental implantation/methods; dental implants; meta-analysis; time factors; tooth extraction; tooth socket/surgery.
Figures
Wismeijer D, Joda T, Flügge T, Fokas G, Tahmaseb A, Bechelli D, Bohner L, Bornstein M, Burgoyne A, Caram S, Carmichael R, Chen CY, Coucke W, Derksen W, Donos N, El Kholy K, Evans C, Fehmer V, Fickl S, Fragola G, Gimenez Gonzales B, Gholami H, Hashim D, Hui Y, Kökat A, Vazouras K, Kühl S, Lanis A, Leesungbok R, van der Meer J, Liu Z, Sato T, De Souza A, Scarfe WC, Tosta M, van Zyl P, Vach K, Vaughn V, Vucetic M, Wang P, Wen B, Wu V.
2018 October - Clin Oral Implants Res.
Group 5 ITI Consensus Report: Digital technologies
Abstract
Objectives: Working Group 5 was assigned the task to review the current knowledge in the area of digital technologies. Focused questions on accuracy of linear measurements when using CBCT, digital vs. conventional implant planning, using digital vs. conventional impressions and assessing the accuracy of static computer-aide implant surgery (s-CAIS) and patient-related outcome measurements when using s-CAIS were addressed.
Materials and methods: The literature was systematically searched, and in total, 232 articles were selected and critically reviewed following PRISMA guidelines. Four systematic reviews were produced in the four subject areas and amply discussed in the group. After emendation, they were presented to the plenary where after further modification, they were accepted.
Results: Static computer-aided surgery (s-CAIS), in terms of pain & discomfort, economics and intraoperative complications, is beneficial compared with conventional implant surgery. When using s-CAIS in partially edentulous cases, a higher level of accuracy can be achieved when compared to fully edentulous cases. When using an intraoral scanner in edentulous cases, the results are dependent on the protocol that has been followed. The accuracy of measurements on CBCT scans is software dependent.
Conclusions:Because the precision intraoral scans and of measurements on CBCT scans and is not high enough to allow for the required accuracy, s-CAIS should be considered as an additional tool for comprehensive diagnosis, treatment planning, and surgical procedures. Flapless s-CAIS can lead to implant placement outside of the zone of keratinized mucosa and thus must be executed with utmost care.
El Kholy K, Freire M, Chen T, Van Dyke TE.
2018 June - Front Immunol.
Resolvin E1 Promotes Bone Preservation Under Inflammatory Conditions
Abstract
Resolvins are endogenous lipid mediators derived from omega-3 fatty acids. Resolvin E1 (RvE1), derived from eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), modulates osteoclasts and immune cells in periodontal disease models. The direct role of RvE1 in bone remodeling is not well understood. The objective of this study was to determine the impact of RvE1 on bone remodeling under inflammatory conditions. Our working hypothesis is that RvE1 downregulates bone resorption through direct actions on both osteoblast and osteoclast function in inflammatory osteoclastogenesis. A tumor necrosis factor-α induced local calvarial osteolysis model with or without the systemic administration of RvE1 was used. To evaluate osteoclastogenesis and NFκB signaling pathway activity, murine bone tissue was evaluated by Micro CT (μCT) analysis, TRAP staining, and immunofluorescence analysis.
Mechanistically, to evaluate the direct role of RvE1 impacting bone cells, primary calvarial mouse osteoblasts were stimulated with interleukin (IL)-6 (10 ng/ml) and IL-6 receptor (10 ng/ml) and simultaneously incubated with or without RvE1 (100 nM). Expression of receptor activator of NFκB ligand (RANKL) and osteoprotegerin (OPG) was measured by ELISA. RNA sequencing (RNA-Seq) and differential expression analysis was performed to determine signaling pathways impacted by RvE1. The systemic administration of RvE1 reduced calvarial bone resorption as determined by µCT.
Histologic analysis of calvaria revealed that osteoclastogenesis was reduced as determined by number and size of osteoclasts in TRAP-stained sections (p 0.05). Immunofluorescence staining of calvarial sections revealed that RvE1 reduced RANKL secretion by 25% (p 0.05). Stimulation of osteoblasts with IL-6 increased RANKL production by 30% changing the RANKL/OPG to favor osteoclast activation and bone resorption. The ratio changes were reversed by 100 nM RvE1. RvE1 decreased the production of RANKL maintaining an RANKL/OPG more favorable for bone formation. RNA-Seq and transcriptomic pipeline analysis revealed that RvE1 significantly downregulates osteoclast differentiation mediated by differential regulation of NFκB and PI3K-AKT pathways.
RvE1 reduces inflammatory bone resorption. This action is mediated, at least in part, by direct actions on bone cells promoting a favorable RANKL/OPG ratio. Mediators of resolution in innate immunity also directly regulate bone cell gene expression that is modulated by RvE1 through at least 14 specific genes in this mouse model.
El Kholy K, Genco RJ, Van Dyke TE.
2015 June - Trends Endocrinol Metab.
Oral infections and cardiovascular disease
Abstract
Oral infections are the most common diseases of mankind. Numerous reports have implicated oral infections, particularly periodontitis, as a risk factor for atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (CVD). In this review we examine the epidemiology and biologic plausibility of this association with an emphasis on oral bacteria and inflammation. Longitudinal studies of incident cardiovascular events clearly show excess risk for CVD in individuals with periodontitis. It is likely that systemic exposure to oral bacteria impacts upon the initiation and progression of CVD through triggering of inflammatory processes. Given the high prevalence of periodontitis, any risk attributable to future CVD is important to public health. Unraveling the role of the oral microbiome in CVD will lead to new preventive and treatment approaches.
Anderson LE, Inglehart MR, El Kholy K, Eber R, Wang HL.
2014 August - Implant Dent.
Implant associated soft tissue defects in the anterior maxilla: a randomized control trial comparing subepithelial connective tissue graft and acellular dermal matrix allograft
Abstract
Introduction: This randomized controlled clinical pilot trial compared the efficacy of 2 soft tissue grafting methods for correcting esthetic discrepancies associated with definitively restored implant crowns.
Methods:Thirteen patients presenting with implants displaying recession, thin biotype, concavity defects, or a combination thereof associated with single crowned dental implants randomly received subepithelial connective tissue grafts (SCTG) in the control group (N = 7) or acellular dermal matrix (ADM) allografts in the test group (N = 6), both under coronally positioned flaps. Data regarding soft tissue, hard tissue, esthetics, and quality of life (QoL) parameters were collected over 6 months.
Results: Both groups gained tissue thickness (SCTG: 63% and ADM: 105%), reduced concavity measures (SCTG: 82% and ADM: 96%), and improved recessions (SCTG: 40% and ADM: 28%) from baseline to 6 months. Clinicians determined improvement in esthetics for both groups (P = 0.001), unlike patients who did not change their esthetic ratings. No statistical differences were noted for QoL assessment; however, ADM subjects had more eventful wound healing (P = 0.021).
Conclusions:Within the limitations of this study, both SCTG and ADM result in increased mucosal thickness, reduction in concavity dimensions, and have a potential for recession reduction on definitively restored dental implants.
Chan HL, El Kholy K, Fu JH, Galindo-Moreno P, Wang HL.
2010 December - Implant Dent.
Implant primary stability determined by resonance frequency analysis in surgically created defects: a pilot cadaver study
Abstract
Aim: Implant primary stability is a prerequisite for implant success. A dehiscence or a circumferential defect (CD) at the time of implant placement presents a challenge for achieving primary stability. The aim of this study was to examine the correlations between implant primary stability determined by resonance frequency analysis (RFA) and periimplant bone levels.
Materials:Ten implants were placed in 2 cadaver heads. A series of different sizes of narrow (NDD) and wide (WDD) dehiscence defects and CDs were surgically created around 6 and 4 implants, respectively. Implant primary stability in each size of the 3 different defect types was measured with RFA. For each defect type, the association between the RFA readings and the defect size was plotted and statistically analyzed.
Results: In NDD study, the RFA readings were not correlated with the defect size. In WDD study, the association was significant for most implants, with the coefficient correlation (r) ranging from -0.88 to -0.97. In CD study, there was also a significant association between the implant stability quotient readings and the bone levels, and the r ranged from -0.94 to -0.99.
Conclusion:The association between implant primary stability measured by RFA and the size of surrounding bone defects was defect type dependent. The correlation was highly significant for WDD and CD but not for NDD.
EJohn V, El Kholy K, Krishna R.
2009 Spring - J Indiana Dent Assoc.
Periodontal maintenance therapy: an integral part of dental practice. Case reports on three periodontally involved patients
Abstract
Periodontal maintenance therapy is an integral aspect of any general dental or specialist practice. Numerous studies have indicated that periodontal therapy in the absence of a carefully designed maintenance program invariably results in the relapse of the disease condition. Accordingly, dental practices that provide periodontal care without a maintenance program deal with significant patient management and disease management issues. In this article, three cases are presented with varying levels of disease severity but all sharing the common trait of having being enrolled in a good maintenance program with positive treatment outcomes.